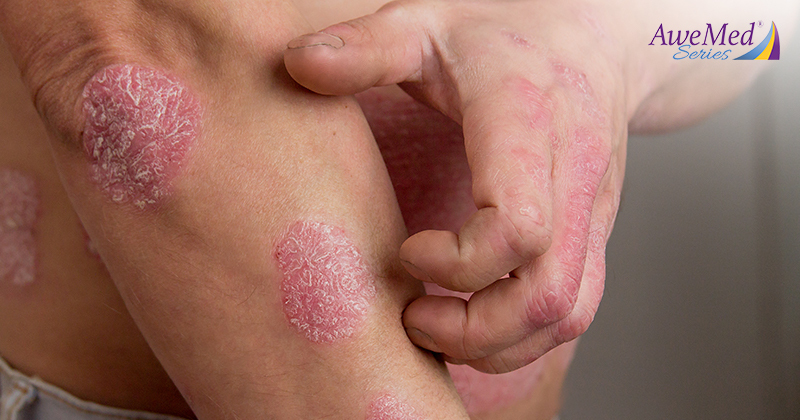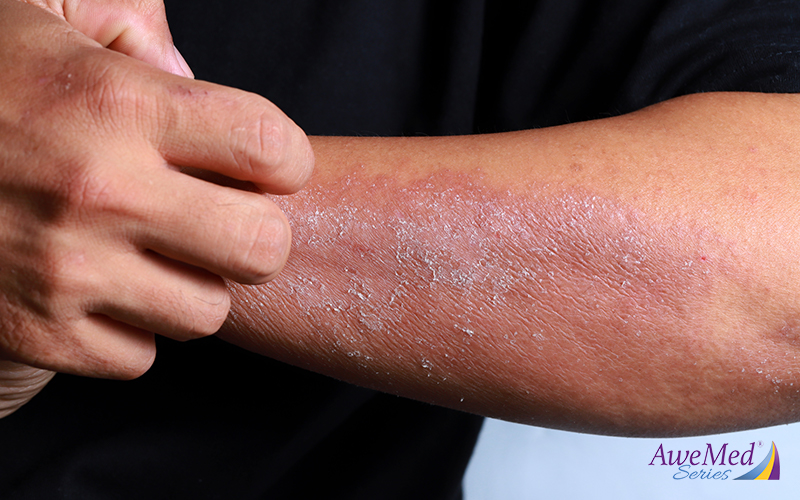
Eczema is a tricky skin condition that can be influenced by your dietary choices. This connection between eczema and diet has been a topic of growing interest and research, and emerging evidence suggests that what you eat can influence its development and severity. While there is no definitive cure for the condition, modifications to your meals can assist in managing it. Read on to learn more.
1. Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Eczema doesn’t stem from food allergies, but these sensitivities can trigger flare-ups. When allergenic foods enter the body, your immune system react by releasing histamines, leading to redness and itchiness. If you suffer from both food allergies and eczema, identifying these triggers and actively avoiding them may help with managing the condition. Some foods commonly known to trigger eczema symptoms include cow’s milk, eggs, wheat, and peanuts.
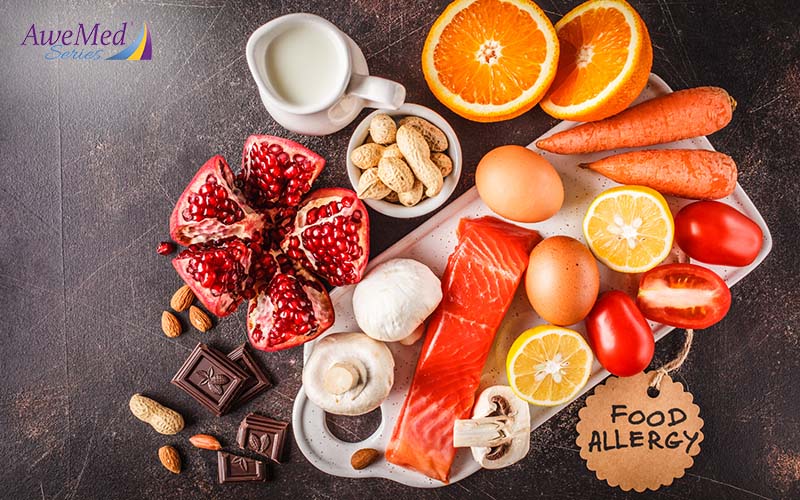

However, excluding these foods from your diet may not necessarily improve or prevent eczema flare-ups. Your best course of action is to approach it with topical solutions such as an eczema cream, and to avoid irritants like soap. Also, work closely with a healthcare professional to establish the causes of your eczema and to create a personalized treatment plan.
Learn More: Soothe the Itch: Experts Share Tips On Managing Eczema with the Right Regimen
2. Inflammatory Response
Certain foods have the tendency to stir up inflammation in your body, contributing to eczema. Processed items laden with additives, artificial sweeteners, sugars, saturated fats, and trans fats are foods to avoid as they can activate an immune response and exacerbate your condition.
Conversely, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish, fruits and vegetables, may reduce eczema flare-ups. These ingredients are packed with omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants that can combat inflammation and contribute to overall skin health.
3. Gut Health
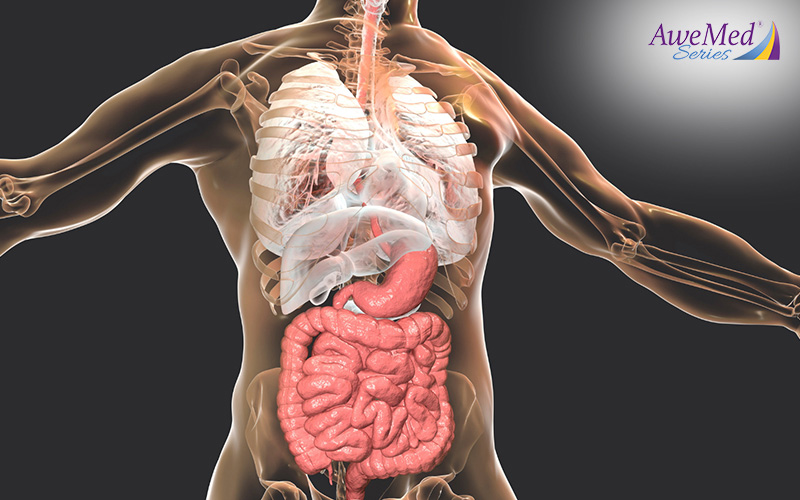
Studies have shown that your gut microbiome—the trillions of microorganisms residing in your digestive tract—has an impact on skin health. Any disruption in the balance of your gut bacteria can increase your risk of developing flare-ups.
To nurture a thriving gut microbiome and healthier skin, moderate your consumption of processed and sugary foods, and introduce more prebiotics and probiotics-rich foods into your meals. The former promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria while the latter contains live beneficial bacteria. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and high-fiber foods like oats and whole grains are some great options.
4. Hydration
Staying hydrated is a simple yet crucial aspect of managing eczema. Although hydration from water consumption does not directly impact skin health, it maintains proper functioning within the body, which helps with fighting inflammation and flushing out waste and toxins. This keeps eczema in control.
For those seeking relief from eczema, adopting a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet can be valuable. However, dietary management alone may not be effective at keeping eczema at bay. It is important to also seek medical advice for a personalized treatment plan and to moisturize your skin regularly with an emollient.
AweMed Series carries a range of products formulated to aid in managing eczema by hydrating your skin. Shop our range of eczema creams and moisturizers here.
References
Food allergies and eczema Information for parents and carers. (n.d.). Retrieved June 28, 2020, from https://www.ouh.nhs.uk/patient-guide/leaflets/files/14460Peczema.pdf
Mahmud, Md. R., Akter, S., Tamanna, S. K., Mazumder, L., Esti, I. Z., Banerjee, S., Akter, S., Hasan, Md. R., Acharjee, M., Hossain, Md. S., & Pirttilä, A. M. (2022). Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995
Douladiris, N., Vakirlis, E., & Vassilopoulou, E. (2023). Atopic Dermatitis and Water: Is There an Optimum Water Intake Level for Improving Atopic Skin? Children, 10(2), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020273