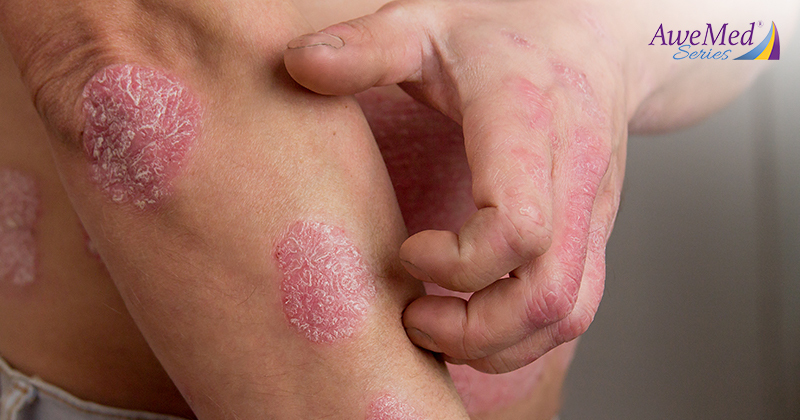
Topical steroids are commonly used in dermatological care, particularly for the management of eczema. However, due to some associated risks, there is considerable debate and controversy surrounding their usage. Are topical steroids safe? Should dermatologists continue to prescribe them to patients with skin conditions? Find out more about them and whether they should be used for eczema below.
What are Topical Steroids?.
Also known as corticosteroids, topical steroids are medications containing synthetic forms of corticosteroid hormones, like cortisol, which are usually naturally produced by the body. How they work is that they suppress the body’s immune response and inflammatory process when applied to the skin, reducing inflammation, itching and redness. These qualities have made them effective for managing skin conditions including eczema, psoriasis, contact dermatitis, and some types of rashes.
Should Topical Steroids Be Used On Eczema?
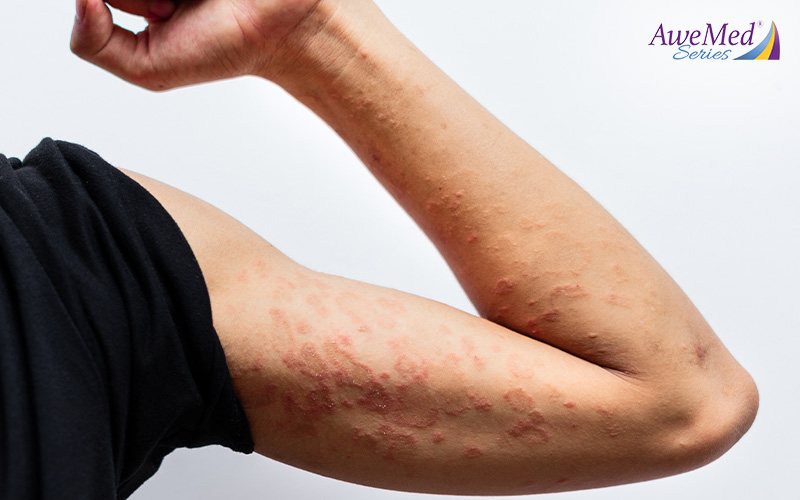
For many years, topical steroids have played crucial roles in the management of eczema and the reduction of inflammation. They provide significant relief from the bothersome symptoms of this chronic skin condition, helping to alleviate redness, swelling, and discomfort while soothing any itchy sensations. They even contribute to the restoration and strengthening of the skin’s natural barrier function to reduce the risk of infection and aid in the body’s healing processes.
However, while topical steroids have proved to be effective for eczema, they can also have negative effects if not used appropriately. Some of the potential problems they can cause include:
- Skin Thinning (Atrophy)
Areas with thinner skin like the face and the groin may experience skin thinning due to the prolonged use of potent topical steroids, becoming fragile and more prone to damage.
- Skin Discolouration
Some changes in skin pigmentation, which can cause the affected skin to become lighter or darker than the surrounding skin, may be experienced.
- Stretch Marks
In some cases, stretch marks may develop on the skin, especially in areas where the skin is already stretched, such as the thighs and buttocks.
- Perioral Dermatitis
When applied to the face, topical steroids may trigger another skin condition known as perioral dermatitis, which causes red, bumpy rashes around the mouth and on the face.
- Topical Steroid Withdrawal
In some cases, when topical steroids are abruptly discontinued after long-term use, individuals may experience a rebound effect, where the eczema symptoms worsen. This can cause topical steroid addiction and withdrawal, leading to a cycle of overuse and dependence on the medication to control symptoms.
How this happens is that the skin, when no longer relying on topical steroids, goes through a reaction that increases nitric oxide levels and the widening of blood vessels. This causes skin erythema.
Topical steroid withdrawal is not a common condition, and you’ll need to consult a doctor to determine if the steroid is the cause of your worsening symptoms. Sometimes, infected eczema can cause them as well. If it’s established that topical steroid withdrawal is the trigger, your doctor will advise you to stop applying steroids and devise an alternative treatment plan.
How To Use Topical Steroids Correctly?
While there are skin sensitivity and infection risks with topical steroids, proper usage can help to prevent them.
- Only use topical steroids once or twice daily on affected areas of your skin.
- Use topical steroids that are suitable for your skin condition. For example, mild options on your face and stronger ones on areas with thicker and less sensitive skin.
- Once your condition is better, cut down the use of topical steroids or switch to non-steroid products, such as lotions and creams for eczema.
Alternatives to Topical Steroids
For those seeking alternative eczema management solutions, there are several options you can consider.

- Emollients and Moisturizers
Regularly applying emollients and eczema relief moisturizers hydrates skin, which reduces dryness and itchiness associated with eczema. Look for eczema creams or lotions that are fragrance free and hypoallergenic.
- Dietary Adjustments
Certain foods can trigger or exacerbate eczema. Keeping a food diary and working with a healthcare provider or allergist to identify and eliminate potential triggers may be beneficial.
- Probiotics
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria, help fortify the immune system and improve the gut microbiome. Some studies suggest that this may have a positive impact on eczema symptoms.
Learn More: Soothe the Itch – Experts Share Tips On Managing Eczema With The Right Regimen
If you or someone you know suffers from eczema, we recommend consulting with a doctor or dermatologist before trying alternative treatments to ensure that they are safe and appropriate. What works for one person may not work for another, so do be patient when finding the most suitable solution.
Eczema-relief products like moisturizers and creams are useful for managing your symptoms. If you’re keen to give them a try, AweMed Series offers a range of lotions and sprays formulated to enhance skin hydration, skin repair, and relieve discomfort. Shop here!
References
Hewett, L. (2022). Topical steroid withdrawal: What the Eczema community needs to know, now. National Eczema Association. https://nationaleczema.org/blog/tsw-need-to-know/
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). (2017, February 23). Eczema: Steroids and other topical medications. InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK424899/
Website, N. (2023b, May 12). Topical corticosteroids. nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/topical-steroids/
Burgess, L. (2023, February 15). Do probiotics for eczema work? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318946